Applying network science to biological research: A new way forward
Data holds the key to solving large-scale health and environmental challenges, but scientists can only truly understand and address the multiple and interlinked contributing factors to these challenges by understanding the complex network of relationships between data - That’s where network science comes in.
Network science is a holistic approach that studies the representation of complex networks and their underlying higher-order interactions in order to establish predictive models of the respective fundamental interactions. As the name suggests, it consists in the exploration and understanding of networks with distinct elements (nodes) and the connections between these elements as links (edges).
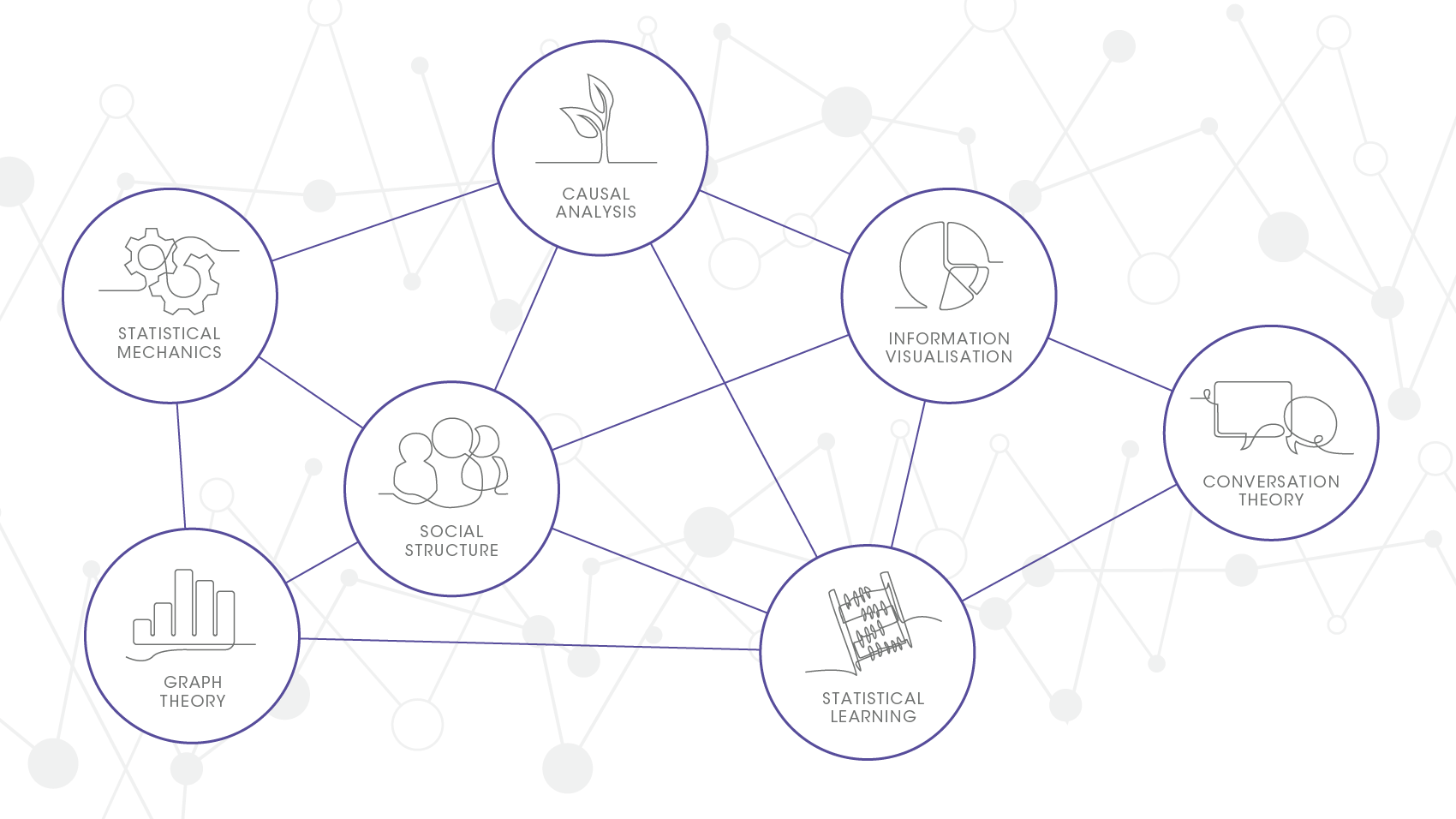
This field of study draws on multiple disciplines including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, social structure from sociology, causal analysis, statistical learning, information visualisation, from computer science, and conversation theory from cybernetics. This unification of subject expertise enables the robust analytical process required to construct and interpret complex network relationships.
One of the most significant use cases for this new science has been to better understand microbiome data. The application of network science via robust analytical tools has played a crucial role in driving recent innovation across numerous sectors.
The complexity and scale of microbiome data
The microbiome plays a critical role in life science-driven innovation across agriculture, nutrition, pharmaceuticals, and any sector associated with the health of animals and humans and the planet.
At a glance, one can observe an emergence of network patterns in how microorganisms operate. Microbiome communities, which include diverse species of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, work together as groups to create a robust environment in which to thrive and ultimately maintain and possibly enhance host health.
Due to the microbiome’s complexity, scale, and perhaps its ability to regulate itself as an ecological network, linear data analysis cannot possibly unlock the true potential of microbiome insights. Robust understanding of the microbiome can only be achieved through the application of network science, which will enable researchers and scientists, across industry verticals to develop innovative products that have a positive impact on human and animal health.
The food industry is transforming
The food industry has shown itself as the industry pioneer for applied microbiome science. Specifically, the functional nutrition sector (see image below) is transforming in response to the evolving market and consumer mindset regarding health and wellness.
![]()
The development of “food as medicine” has become a growing trend in the food industry, where multiple large-scale organisations are motivated to develop functional nutrition for the treatment and prevention of numerous diseases. Recently, scientists have begun exploring the potential of the microbiome to inform the development of these functional foods.
As previously described, network science brings a new perspective by linking different data sources together, leading to the identification of patterns of relationship between elements. Within functional foods, network science will enable the establishment of links between food ingredients that can help the metabolism suppress certain competitive species residing in the gut - a relationship that would have been undetected via linear analysis.
A greater understanding of these links will eventually inform the relationships between the nutrients we ingest and various chronic conditions, including malnutrition, obesity, depression, and beyond. Application of network science can enable scientists, researchers, and innovators to develop functional foods and novel ingredients to improve consumer health through nutrition.
Cargill Health Technologies invests in network science
Chuck Warta, President of Cargill Health Technologies and a leader in food innovation, believes that the company can benefit greatly from applying network science to its data via Eagle Genomics’ platform.
Cargill has generated decades worth of microbiome data on its livestock which was analysed using Eagle Genomics’ e[datascientist] platform. Research into the datasets yielded insights into the animal gut which can potentially be used to enhance animal health and to develop nutrient-rich feed. Improved animal health ultimately leads to improved consumer health, driving better outcomes throughout the food value chain.
Understanding animal health in order to develop nutrient-rich feed is just one area where the food industry can benefit from the application of the microbiome and network science. By bringing these tools into the innovation pipeline, scientists can develop robust scientific product claims targeting gut-associated wellness, and improving overall health.
Science led innovation via causal network science
Food innovation is a fantastic testing ground for the application of network science to biology. But the world is faced with even greater challenges such as soil desertification, reduced plant biodiversity, and increasing rates of metabolic disease. These complex issues similarly necessitate the holistic approach enabled by network science.
Research and product claims in the life sciences require the production of strong, objective evidence. But these data often remain complex, siloed, and overwhelming in volume rather than connected and available for collaborative exploration.
Eagle Genomics brings radical innovation to step-change outcomes by enabling enterprises to meaningfully harness their data. The e[datascientist] platform combines network science, AI, and multiplayer hypergraph technology to allow scientists to identify and test valuable hypotheses, discover connections, and generate insights which can lead to valuable and innovative product claims.
Have a look at the e[datasicentist] platform for the food industry for more detail.